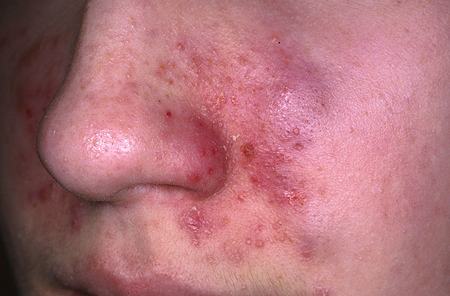
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin disease, but there is no clear-cut diagnosis for it. Although the disease affects 11.6% of the general population, it usually first appears as dry, greasy scalp flakes. It can also develop into red and scaly plaques on the upper lip and sides of the nose. Some people with the disease also develop a conjunctivitis. Generally, individuals with this condition are young, but sometimes it strikes people at a later age.
Cradle cap is one of the most common forms of seborrheic dermatitis. This skin disorder is characterized by scaly, greasy patches on an infant’s scalp. It can also form on an infant’s bottom. The condition is sometimes mistaken for diaper rash. Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitia include a greasy, scaly or flaky patch on the cheeks, eyebrows, mid-chest, and upper back.
In adults, seborrheic dermatitis may present as a generalized eczema. It can also be localized in the scalp and hair. It is most prevalent in Caucasians and infants under three months. However, it can also affect adults in their late twenties and early forties. It has no known cause and no genetic predisposition.
While the exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is not known, it increases the chances of developing it. If a close family member has the disease, your risk is increased. There are no signs or symptoms to indicate the presence of this disease in most people. Your doctor will perform a physical exam and examine your skin. He may perform a biopsy, a procedure that involves scraping a sample of skin cells.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a papulosquamous disorder that affects the skin. It is associated with immune disorders and complement activation. The severity of the condition can vary from mild dandruff to exfoliative erythroderma. A patient with seborrheic dermatitis in the body may experience it in a different area than the one where it first appeared.
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis may be similar to those of other skin conditions, so it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Several different treatments are available. For the most severe case, a prescription may be needed. Behavioral therapy is often recommended, but is not required for severe cases. Depending on the severity of the condition, you may need to visit a dermatologist for follow-up care.
Seborrheic dermatitis can affect any part of the body. While it is often associated with the face and scalp, it can occur anywhere on the body and is not caused by poor hygiene. Unlike diaper rash, seborrheic dermatitis is usually harmless and resolves on its own within a few months. If you have a rash that appears on the skin, you may have seborrheic dermatitis.
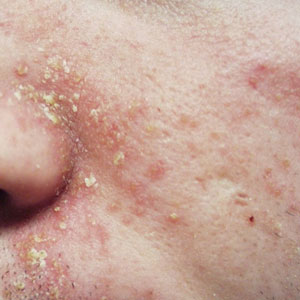
In severe cases, scaly spots disappear. They may be yellowish or white. The affected areas may be greasy and oily. The affected areas may also be red. The skin in these places can be irritated. Despite the severity of the disease, there are treatments for seborrheic dermatitis. These drugs are effective for treating this condition.
The first stage of seborrheic dermatitis is a scaly, crusty skin disease in which skin develops over areas with sebaceous glands. As a rule, seborrheic dermatitis occurs on the face and armpits. The skin in this area becomes red and itchy, and the flaky patches may also flake off. There is no cure for this disease. In severe cases, it can persist for many years without any treatment.
In most cases, seborrheic dermatitis is treated with topical antifungal shampoos. In severe cases, a dermatologist may prescribe a corticosteroid or antibiotic. In severe cases, topical steroids are also used. A dermatologist should diagnose seborrheic dermatitis if it is contagious. If symptoms persist, site somosmass99.com.mx may suggest a treatment that is not allergic to the cause of the rash.
The best treatment for seborrheic dermatitis is a combination of medications. This can help alleviate the condition of the skin. The most common treatment involves a combination of drugs and therapy. A combination of treatments is often recommended for the best results. The condition will improve over time with treatment. It is best to seek medical attention for any recurring outbreaks if they persist. Treating seborrheic dermatitis in children is not recommended, as it can lead to more serious complications.